An important progress has been made in the study of superconjugated nitrogen-containing heterocyclic organic electrode materials and their reaction mechanism. The paper is published in Nature Energy
Recently, Prof. Yong Yang's research group and Prof. Kian Ping's research group from National University of Singapore have made important progress in the research of novel organic electrode materials and their reaction mechanism for rechargeable lithium batteries. Reversible Multi-electron Redox Chemistry of π-conjugated N-containing heteroaromatic molecules-Based Organic Cathodes, 2017, 2, 17074; DOI: 10:10 38 / nenergy. 2017.74
Organic electrode materials have become one of the hot spots of the new generation of flexible batteries and energy storage batteries because of their high mass specific capacity, environmental friendliness, renewable and special-shaped processability. Due to the weakness of organic electrode materials, such as low electronic conductance and poor cycling performance, many difficulties are encountered when they are applied to commercial applications. This research chooses a nitrogen functional groups as electrochemical activity, successful synthesis of a class of large PI conjugate melamine sinensis oh Lin Quinoxaline derivatives, the material in the potential range of 1.2 3.9 V, 400 ma/g under the condition of current density, reversible charge and discharge capacity of 395 mah/g, and under the current density of 8 a/g, after 10000 times of charge and discharge cycle, capacity rate can reach 70%. More importantly, the electrochemical reaction mechanism of multi-step lithization of the compound was clearly analyzed by using 15N labeled high resolution solid state NMR technique and assisted by theoretical calculation results, which provided important theoretical guidance and characterization methods for the understanding and development of this novel organic electrode materials.
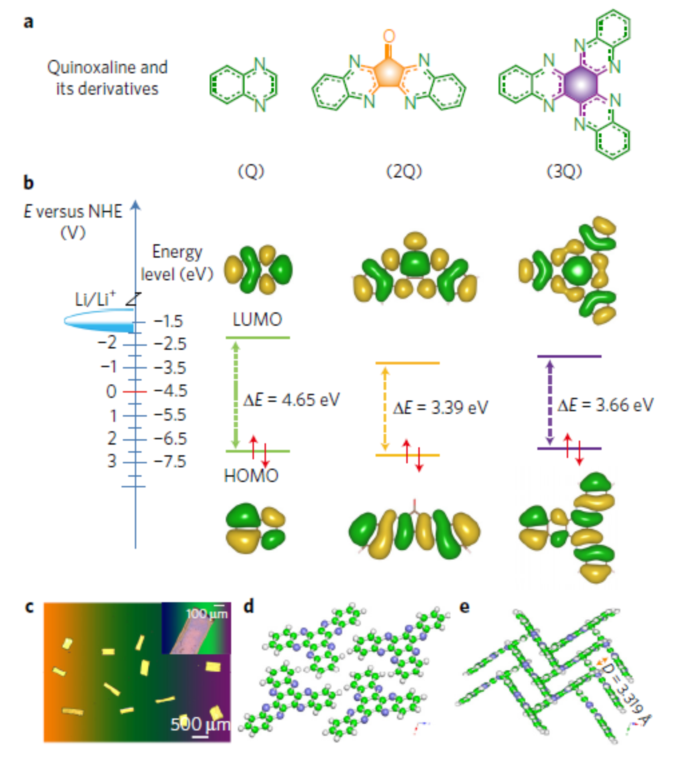
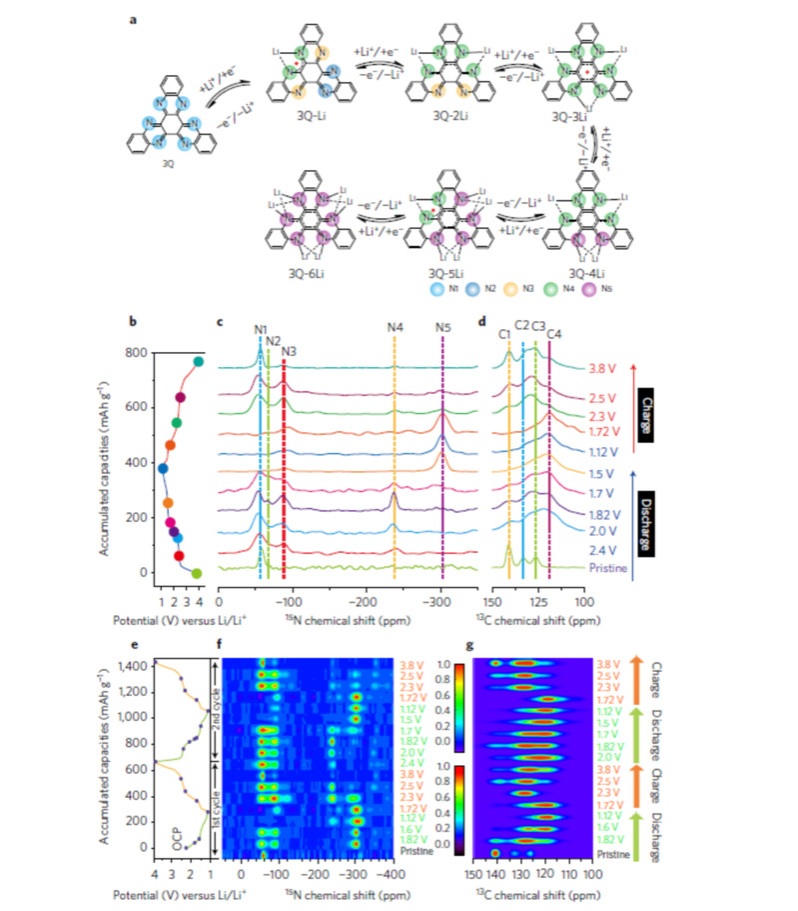
Figure 1 Molecular structure, energy band diagram and single crystal morphology of quinoxaline and its dimer and trimer
Figure 2 The reaction mechanism of multistep one by one lithiation of tripolyquinoxaline and its process corresponding to 15N, 13C solid NMR谱
The research group of Prof. Yong Yang has been engaged in the research of electrode materials and solid NMR technology for lithium/sodium ion battery for a long time. In recent years, many outstanding research achievements have been made in the new electrode materials, solid electrolyte and the application of solid NMR technology (e.g. Chem. Mater., 2016, 28 (4), 1026-1033; 2015, 27, 5736-5744; 2015; 27, 6650-6659; ACS Applied Mater. & Interfaces, 2016, 8, 22227-22237; J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 2016,4, 9054-9062; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016,55, 10717-10721); Professor Yong Yang has been invited to give invitation reports at international academic conferences for several times in the past three years, and served as a member of the academic committee of several international academic conferences. He has also been invited to serve as the editor-in-chief of the international academic journal J Power Sources since June 2016.
The above research work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21233004) Interface Electrochemistry Innovation Group (No.21621091), the National Key Fundamental Research and Development Program (No. 2016YFB0901502), the State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces and its Collaborative Innovation Center for Energy Materials Chemistry.
Paper link:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nenergy.2017.74
